How Generative AI is Shaping the Future of Insurance
by Kirill Fainshmidt, Solution Consultant, Finance Practice, DataArt
Generative AI is revolutionizing the insurance industry, offering unprecedented operational efficiency and customer service advancements.
Within the sector, there is a clear shift toward integrating open-source models and rethinking privacy and security practices to meet evolving policies and compliance standards. These changes mark a move from theoretical discussions to tangible applications as firms take steps toward making generative AI mainstream.
Moreover, generative AI bridges the gap for knowledge workers by simplifying access to extensive qualitative data, which was previously difficult to process. This has made the development of training data sets possible, facilitating the creation of models tailored specifically to the insurance industry.
Yet, integrating generative AI into more intricate insurance processes hinges on technology and human acceptance. The welcoming attitude of some professionals towards new technologies is crucial for its broader adoption. Luckily, some companies are already deploying advanced chatbots and underwriting automation tools, achieving greater efficiency in insurance operations.

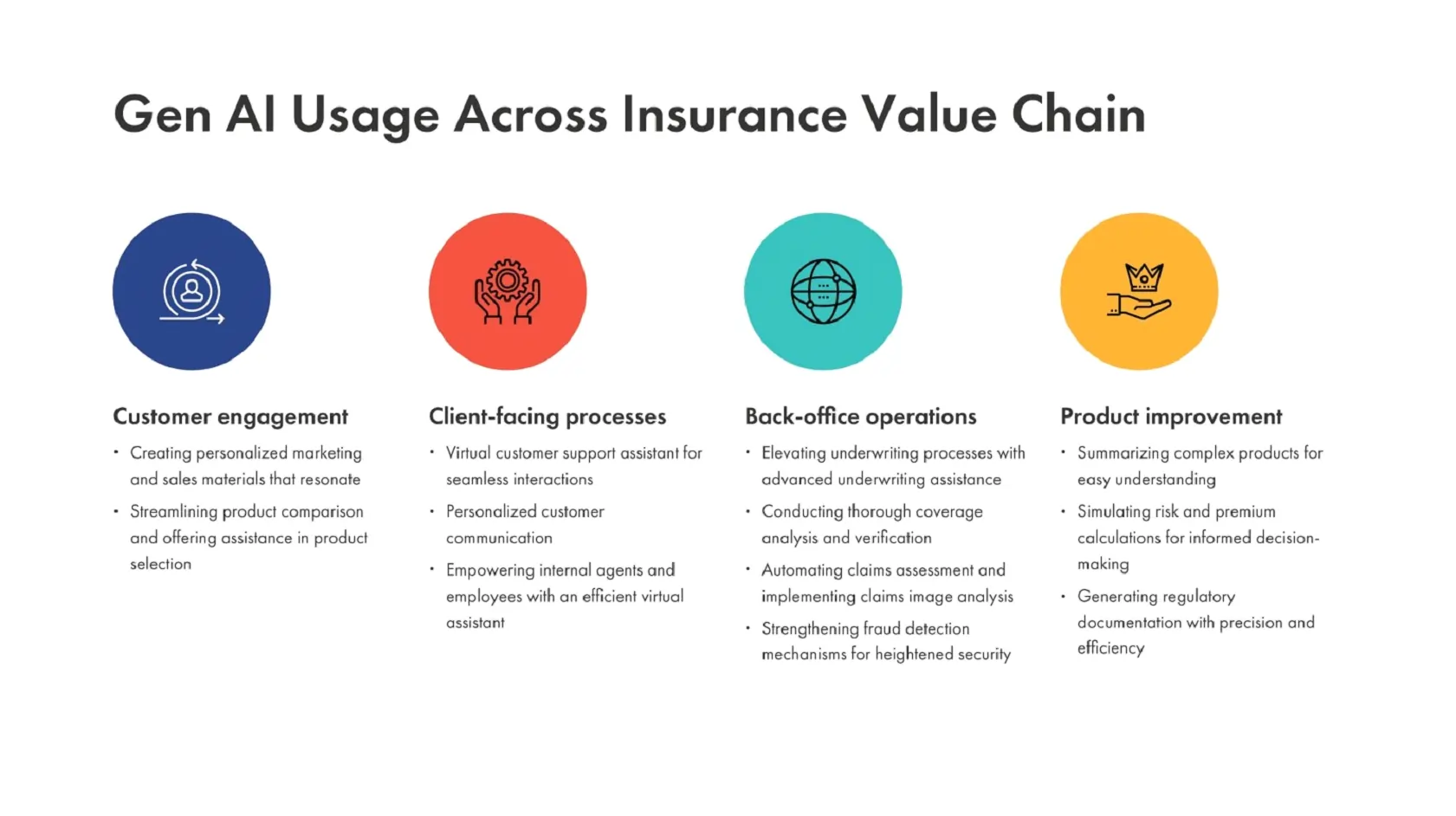
Tackling Industry Pain Points with Generative AI
Streamlining Onboarding: Onboarding traditionally suffers from delays and redundancies, affecting morale and customer satisfaction. On average, new employees take 10-12 weeks to become fully operational, with vast amounts of time dedicated to administrative tasks. Generative AI can streamline these procedures, potentially shortening the timeline by up to 30% and enhancing employee integration and satisfaction, which is critical to growth and maintaining a competitive advantage.
Optimizing Customer Support: Innovation has opened new frontiers for client engagement. Virtual assistants now provide non-stop assistance, delivering consistent service and tailored communication. On the flip side, our staff benefits from AI tools that boost their productivity. Traditional support systems can be overwhelmed by repetitive inquiries, leading to slow service and increased operational costs. With routine questions taking up around 80% of support time, generative AI can address up to 70% of these questions, potentially reducing costs and freeing support teams to focus on more complicated issues.
Simplifying Policy Interpretation: Behind the scenes, generative AI aids underwriters, expedites coverage checks, improves claims processing through automation and image analytics, and fine-tunes fraud detection. Reading insurance policies is complex, often causing mistakes and disputes. Misinterpretations can escalate conflicts by 10-15%. With up to 90% accuracy in extracting policy details, generative AI facilitates more transparent comprehension and decision-making, reducing misinterpretation.
Generative AI doesn’t just analyze policies accurately—it transforms complex insurance offerings into comprehensible summaries and enables insightful risk and premium assessments. It also generates regulatory documents with unparalleled precision and efficiency.
This trajectory is gathering pace. By 2026, forecasts suggest over 80% of enterprises will incorporate generative AI in some form, a significant jump from less than 5% today.
Prominent Generative AI Use Cases in Insurance
The impact of generative AI in the insurance sector is evident across various segments, leading to marked improvements in efficiency and productivity.
- In the Auto Insurance Managing General Agent (MGA) space, introducing AI-driven virtual assistants and chatbots has improved customer service. By handling a substantial volume of inquiries in real-time, these tools have cut down on the need for traditional email support by over 50%. This shift boosts customer satisfaction and allows for a more strategic allocation of workforce resources.
- Specialty insurance companies are also capitalizing on generative AI to automate intricate underwriting processes, experiencing a surge in productivity that exceeds 100%. The time required for critical underwriting activities has significantly decreased, affording these companies the agility to respond swiftly to new opportunities and customer requirements.
- Advanced generative AI systems have been instrumental in streamlining claims settlements within Digital Insurance. A standout instance saw claim resolutions and associated payments executed in a dramatically shorter timeframe than the industry norm, setting a new standard for process efficiency and quick service that significantly benefits customer relationships and operational efficiency.
These targeted applications of generative AI highlight a clear trend: the technology is creating tangible improvements in the insurance industry, transforming what were once complex tasks into streamlined operations that strengthen customer trust and elevate service standards.
Limitations of GenAI
Acknowledging the promise of generative AI within the insurance industry also means recognizing the hurdles it presents—not as setbacks but as complexities to be managed. These challenges speak to the nuances of implementing advanced technologies in spaces governed by stringent requirements and diverse needs.
The risks associated with AI models are not always clearly defined due to the vast range of applications and the difficulty in evaluating their impact. Enthusiasm for adopting these models is driven by their clear advantages, such as process automation and the possibility of long-term cost savings. However, there is a general lack of understanding across the industry regarding the potential risks, as there hasn’t been enough time to evaluate these models over extended periods.
Since generative AI operates on large datasets, there is an ever-present challenge associated with data integrity: the completeness and moral, compliance, or regulatory alignment of the data. With differing requirements worldwide, the uncertainty grows, potentially leading to biased or inequitable outcomes from the models. It’s crucial for operators to continually check and adapt these systems’ outputs to ensure they meet project specifications.
On the regulatory and legal front, the implications are currently substantial and demand cautious consideration by organizations. For example, the European Union is developing laws stipulating which data is suitable for input into these models. In the meantime, companies must diligently manage what goes into these models to avoid compromising compliance policies.
When problems with outputs arise, tracing them back to their origins is a formidable task, considering the extensive size of the initial datasets, which may range between 7-20 terabytes. Identifying which aspects of the source data led to suboptimal results is complex, highlighting a need for sophisticated analysis and troubleshooting techniques.
Furthermore, these AI systems’ maintenance and risk management may necessitate entirely new professional capacities, such as those specializing in prompt engineering. These roles focus on crafting the most effective queries for the models, a crucial process for eliciting the best possible outcomes from the AI.
As the insurance industry moves forward with integrating generative AI, it becomes increasingly important to foster an environment where technology, risk management, and regulatory compliance intersect coherently, ensuring that deploying these technologies is as responsible as it is transformative.
Looking at the Future of GenAI
As employees continue to adopt generative AI tools for daily tasks, the technology is anticipated to grow in its capacity for creativity and problem-solving. Moreover, the expansion into multimodal capabilities, handling text, images, and videos, will further transform the utility of AI applications in insurance, broadening the scope for innovation and enhancing services like document processing and chatbot interactions.


